

This Month's Oddity in the News:
A Modern-Day Man
Contracts the Black Plague
(in 2012, not 1348)
IN THE ARCHIVES:
Amelia Earhart
Ugly Buildings
Road Zombies
Frozen Dead Guy Days in Colorado
Mind Reading
Largest Tumor
Birdseed Spell Gone Wrong
Conjoined Twins
Two-Faced Cat Makes Record
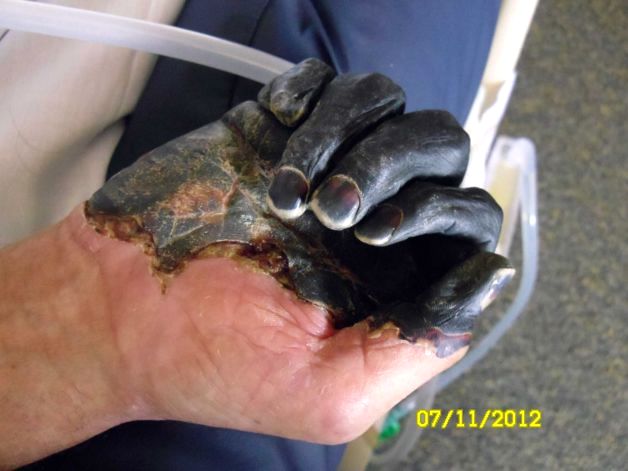
Paul Gaylord contracted the disease when he tried to pull a mouse out of the mouth of his cat, Charlie, because it was choking on the rodent. The disease, a version of the medieval scourge that wiped out at least a third of Europe, took away the 59-year-old welder's fingertips, his toes and his ability to make a living. He faces an arduous recovery surrounded by constant reminders of his misery, the infected cat died, and the trailer he's living in has a mouse problem.
See the entire article HERE
PORTLAND, Oregon July 17, 2012 (AP) — One look at Paul Gaylord's hands shows why the plague is referred to as "Black Death."
The welder's once-strong hands have been withered by the cell-killing infection and darkened to the color of charcoal. Doctors are waiting to see if they can save a portion of his fingers, but the outlook is grim for the man who needs them for his livelihood.
"I don't think I can do my job," Gaylord said in a phone interview from a Bend, Ore., hospital. "I'm going to lose all my fingers on both hands. I don't know about my thumbs. The toes — I might lose all them, too."
Gaylord, who turns 60 next month, contracted a rare case of the plague trying to take a mouse from the jaws of a choking cat at his home in Prineville, in rural Oregon.
He faces a difficult recovery now that he's out of intensive care. His family is trying to raise money to get him into a new house, because the manufactured home he was living in has a leaky roof, a moldy bathroom and mice — dangerous living conditions for a man with a weakened immune system.
"We didn't even know the plague was around anymore," said his sister, Diana Gaylord. "We thought that was an ancient, ancient disease."
The bacterium that causes the plague is carried by fleas, which can infect people and animals. The disease that killed millions in the Middle Ages is extremely rare in current times — an average of seven cases occur in the U.S. each year.
Gaylord's illness began after he saw a stray cat — who he'd named Charlie — with a dead mouse jammed in the back of his throat. The cat appeared to be choking, so Gaylord and a friend attempted to dislodge the mouse.
The distressed cat bit his hand. Unable to remove the mouse, Gaylord shot Charlie to end his suffering and buried him in the yard.
Two days later, he awoke with a fever and chills.
An Army veteran who rarely visits a doctor, Gaylord felt sick enough to go to the Veterans Administration outpatient clinic in nearby Bend. But the clinic had so many patients that doctors couldn't see him for more than a week.
The next day, Gaylord, who doesn't have private health insurance, went to an urgent care clinic. The doctor diagnosed cat scratch fever, provided him with medicine and told him to return if his condition worsened.
He was back a few days later. Diana Gaylord said her brother dripped with sweat and his lymph nodes swelled.
"He had a lump under his arm swollen almost as big as a lemon," she said.
A doctor at the urgent care clinic sent him in an ambulance to St. Charles Medical Center in Redmond. There, a doctor diagnosed the plague, and Gaylord was taken to a larger hospital in Bend.
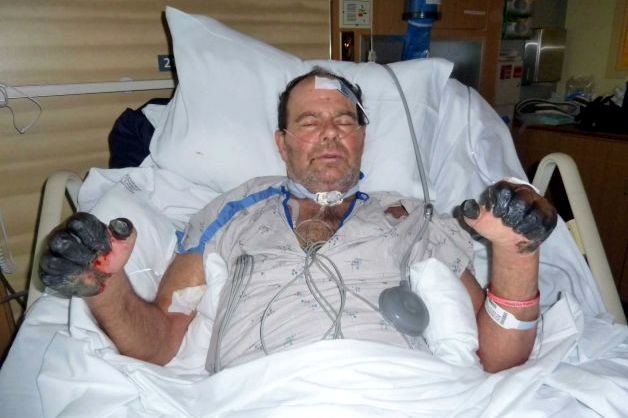
Gaylord spent nearly a month on life support and only recently left the intensive care unit. At one point, doctors thought he was going to die, said Debbie Gaylord, his wife.
A hospital chaplain baptized the unconscious patient and Gaylord's son, Jake, arrived from Austin, Texas, to say goodbye.
Hours later, doctors told his family that he had improved.
"Jake got here and all of sudden the next morning he started getting better," said Andrea Gibb, Gaylord's niece. "The doctors were like kids in a candy store. They were so excited."
Gaylord's case is Oregon's fifth since 1995. None has been fatal.
The cat's body was dug up, and tests confirmed it had the plague. Other cats and dogs in the area were tested and none had the disease, said Karen Yeargain of the Crook County Health Department.
Gaylord is slowly getting better. He is now able to take strolls through the hospital with the aid of a walker, and the family hopes he can return home by October.
UPDATE: Yet another NEW case of plague HERE
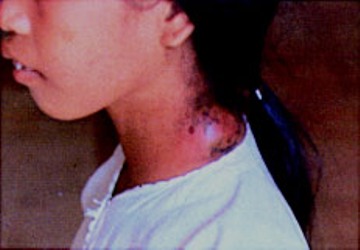
TODAY THE BUBONIC PLAGUE CAN BE TREATED WITH ANTIBIOTICS
The Bubonic Plague is still carried by fleas that infect rodents today but is very uncommon in the United States
WHAT IS THE PLAGUE?
Bubonic plague is a zoonotic disease, circulating mainly among small rodents and their fleas, and is one of three types of bacterial infections caused by Yersinia pestis (formerly known as Pasteurella pestis), which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Without treatment, the bubonic plague kills about two thirds of infected humans within 4 days.
The term bubonic plague is derived from the Greek word βουβών, meaning "groin." Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) especially occur in the armpit and groin in persons suffering from bubonic plague. Bubonic plague was often used synonymously for plague, but it does in fact refer specifically to an infection that enters through the skin and travels through the lymphatics, as is often seen in flea-borne infections.
Bubonic plague—along with the septicemic plague and the pneumonic plague, which are the two other manifestations of Y. pestis—is generally believed to be the cause of the Black Death that swept through Europe in the 14th century and killed an estimated 25 million people, or 30–60% of the European population. Because the plague killed so many of the working population, wages rose and some historians have seen this as a turning point in European economic development.
See the entire article HERE
